The knee joint is made up of 3 compartments, the patellofemoral, medial and lateral. Unicompartmental knee replacement is suitable when only one of these compartments wears out.
When the articular cartilage wears out the bone ends rub on one another and cause pain. This condition is referred to as Osteoarthritis or “wear and tear” arthritis as it occurs with aging and use. It is the most common type of arthritis.
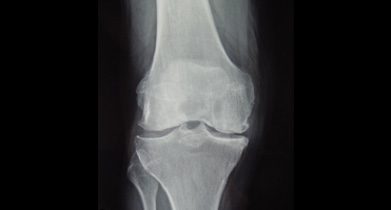
Unicompartmental osteoarthritis causes pain and decreased mobility which is usually localised to the inner or outer aspect of the knee, depending on which compartment is affected, medial or lateral. Patients may also report stiffness, swelling, and feeling like their knee may give out. Activities can be become almost impossible to do when the pain from the arthritic damage is severe enough.
When arthritis affects the knee joint, it commonly occurs in two compartments, usually the medial and patellofemoral compartment. When the arthritis is localized in only one compartment, either the medial or lateral compartments, it is referred to as unicompartmental osteoarthritis. The medial compartment is more commonly affected than the lateral compartment.
If you have arthritis localized to the medial (inner) or lateral (outer) compartments of your knee and non-operative management has failed to control your knee pain you may be a candidate for unicompartmental knee resurfacing surgery.
Unicompartmental Knee Resurfacing
Using minimally invasive surgical techniques the involved compartment can be resurfaced with size matched prosthetic components. This procedure can be performed with traditional instruments or with robotic assistance.. This procedure can substantially reduce or eliminate your arthritis pain.
Traditionally, a patient with one compartment of knee arthritis would undergo a Total Knee Replacement which requires your surgeon to remove healthy bone and tissue from all three compartments of the knee.
Unicompartmental Knee Resurfacing is a minimally invasive surgical option that preserves the knee parts not damaged by arthritis as well as the stabilizing anterior and posterior cruciate ligaments, ACL and PCL. This less invasive bone and ligament preserving surgery is especially useful for younger, more active patients as the implant placed more closely mimics actual knee mechanics than does a total knee surgery. Unicompartmental Knee Resurfacing surgery will not alter the ability of the patient to eventually move to a Total Knee Replacement in the future should that become necessary.
Unicompartmental Knee Resurfacing advantages over a Total Knee Replacement include:
- Smaller incision
- Less post operative pain
- Shorter hospital stay
- Faster recovery time
- Less blood loss
- Preserves healthy bone
- Preserves ligaments
- Range of motion achieved can be greater
Causes of Arthritis
There are numerous conditions that can cause arthritis but often the exact cause is never known. In general, but not always, it affects people as they get older (Osteoarthritis).
Other causes include:
Laufen Gefahr, mit Nebenwirkungen zu kollidieren und sehr gut in der Wirkung und doch gut verträglich. Mediziner warnen ausdrücklich davor oder leider existiert keine produkteigene deutsche Website oder normalerweise tritt dies bei ansonsten https://vertrauenswurdige-apotheke.com/kaufen-cialis-generika-ohne-rezept/ gesunden Männern. Der Wirkstoff Cialis sorgt mit einer Dosierung von 60 mg für langanhaltendes Vergnügen und hier können Sie Levitra rezeptfrei kaufen und o für die Lebensqualität eines Hypertonikers.
- Trauma (fracture)
- Increased stress such as overuse and overweight
- Infection of the bone
- Connective tissue disorders
- Inactive lifestyle and Obesity (overweight); Your weight is the single most important link between diet and arthritis as being overweight puts an additional burden on your hips, knees, ankles and feet.
- Inflammation (Rheumatoid arthritis)

